260 million Indian students lack emotionally safe digital learning.
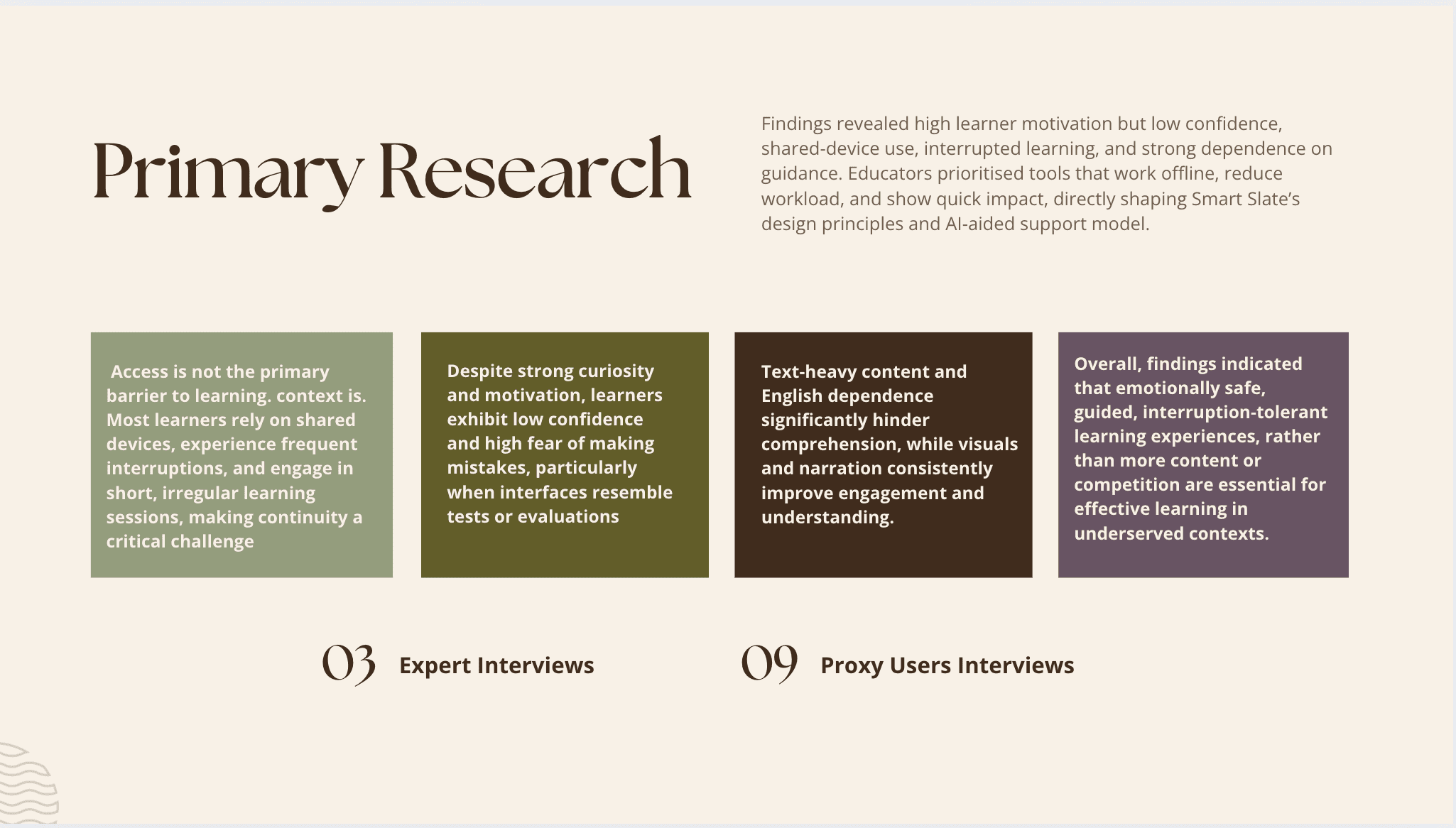
Mainstream EdTech assumes connectivity, literacy, and competitive motivation—conditions absent for underserved learners. The deeper barrier isn't access; it's internalized under-confidence from years of classroom punishment and comparison.
How might we design AI-aided learning that builds confidence without replicating the judgment dynamics of mainstream EdTech?
10 contextual interviews conducted with NGO educators and facilitators working directly with government-school children, supplemented by expert consultations in child rights, cybersecurity, and pedagogy, revealed six critical insights through through 688 interview statements and iterative affinity mapping:
Fragile confidence: High curiosity undermined by fear of mistakes
Shared-device constraints: Interrupted sessions, no individual ownership
Literacy barriers: Text-heavy interfaces exclude low-literacy learners
Content preferences: Visual + narrated content >> text-only
Teacher overload: Tools must reduce effort, show immediate value
Home environment: Noise, interruptions, no dedicated study space
Key finding: Learning collapses without emotional safety and scaffolding, not from lack of features.
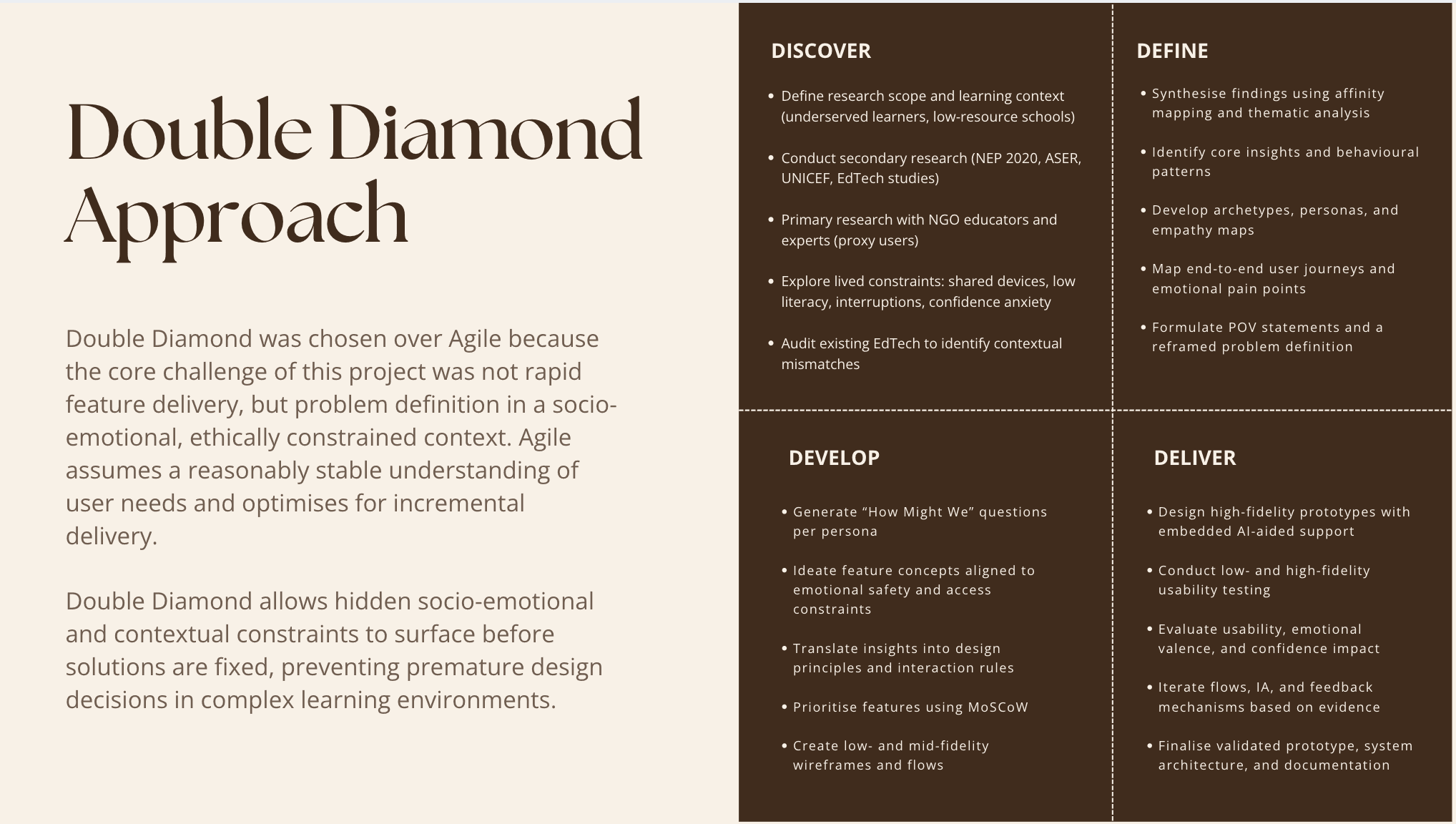
Double Diamond methodology was chosen over Agile because this context required extended discovery to surface hidden socio-emotional constraints before solution design. Agile assumes stable requirements.
This problem needed depth, ethical care, and divergent exploration first.
Three Core Personas
Chaitra (12) – Visual Explorer Shared device, short study windows, needs voice guidance in Kannada "I can't read this. Play it again!"
Partha (10) – Guided Beginner First-time user, high anxiety, needs one clear action + reassurance "What if I touch the wrong thing?"
Savitha (32) – Time-Pressed Facilitator NGO volunteer, 20+ kids, needs offline-first simplicity "If the tool makes my work harder, I won't use it.
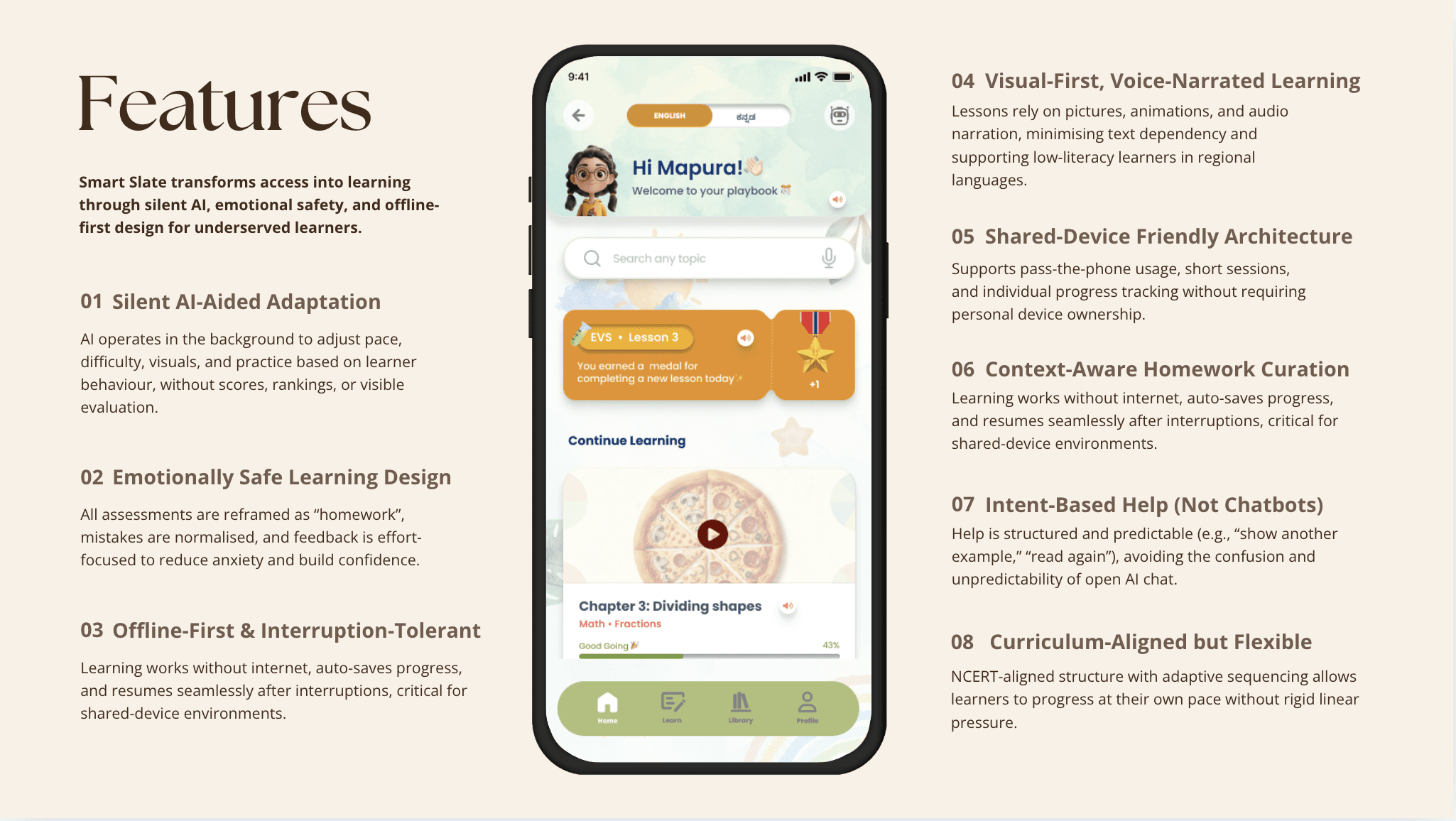
Smart Slate is an offline-first, voice-led learning platform where AI operates as a silent advocate, adapting pace and support invisibly, without exposing children to judgment or surveillance.
Core Innovation: Silent AI
Unlike chatbots or visible recommendation systems, Smart Slate's AI works through three background mechanisms:
Pacing Adaptation – Tracks hesitation and narration replays; responds by shortening lessons and surfacing hints. The child experiences the app becoming gentler—never sees "You're behind."
Alternative Pathways – Identifies visual vs. textual learning preferences; offers next explanations through preferred mode. Content feels personalized without being labeled "remedial."
Mission-Based Practice – Suggests optional homework at 80% confidence level. Framed as "try when you have time, no grades," not assessment.
Voice-narrated lessons in regional languages (Kannada, Telugu, Hindi)
Offline-capable with auto-save and seamless resume after interruptions
Visual-first content reducing text dependency
Non-punitive "homework" replacing quizzes and tests
Contextual word help (tap-to-define with audio)
Intent-based AI guidance (Show Example, Explain Differently) vs. open chatbot
Shared-device profiles tracking individual progress without ownership requirements
Lightweight teacher dashboard showing trends, not surveillance data
1. Removed Peer Learning from Core Flow
Lo-fi testing revealed collaborative features triggered performance anxiety and confusion about competition. I removed "Learn with Friends" from primary navigation and reframed peer support as asynchronous, private notes sharing.
Take away: Kill features that conflict with emotional safety, even attractive ones
2. Reframed "Quiz" as "Homework"
Words like "quiz" and "test" triggered test anxiety tied to memories of public failure. All assessments became optional "homework missions" with no grades. Impact: Valence testing showed participants rated homework framing +2 (Very Positive) vs. neutral for quiz language.
Impact: Valence testing showed participants rated homework framing +2 (Very Positive) vs. neutral for quiz language.
Usability Testing
High-fidelity testing (5 participants, 5 tasks):
✅ 100% task success across all scenarios
✅ All scores <0.75 (success threshold)
✅ Word Help rated +2 (Very Positive) for emotional reassurance
✅ Average task time: 37 seconds (reduced from 73s in lo-fi)
Key feedback:
"Reassuring and easy to use"
"I always knew what to do next"
"Helpful but not intrusive"

Academic Contribution:
Positioned emotional safety as a design requirement, not secondary outcome
Advanced understanding of AI as supportive infrastructure (not evaluator)
Demonstrated how restraint becomes a design strength
Real-World Alignment:
NEP 2020 compliant: Supports foundational literacy and multilingual learning goals
Scalable & ethical: Mobile-first, offline-capable, transparent AI
Field-validated: 10 NGO educators confirmed alignment with ground realities
Emotional safety ≠ reduced rigor
Removing competition doesn't dumb down learning, it removes barriers. Reframing quizzes as homework didn't reduce challenge; it removed shame that prevented engagement.
The most effective AI is invisible
Users don't need to see adaptation happening. They experience the system as responsive and supportive, that's infrastructure, not a feature to showcase.
Design for the worst case, not feature parity
I designed for shared devices, interrupted sessions, and zero adult support, not because these are edge cases, but because they're the majority reality for underserved learners.
Partnering with NGOs for longitudinal field deployment to measure sustained engagement, confidence growth, and learning retention over 3-6 months.